Over 70% of customer experience leaders struggle to design projects that boost loyalty and deliver results. Call center agent performance metrics help tackle these challenges by providing actionable insights into agent productivity, customer satisfaction, and operational efficiency.
By focusing on key indicators like first-call resolution and customer satisfaction scores, businesses can better align their operations with customer expectations, ensuring measurable outcomes and fostering long-term growth.
In this blog, we’ll explore key call center agent performance metrics and how to ultimately track and optimize them to deliver exceptional customer service.
Table of Contents
ToggleWhat Are the Metrics for Call Center Agent Performance?
Call center performance metrics are essential benchmarks that assess how effectively agents meet business goals and customer expectations. They enable organizations to track efficiency, identify improvement opportunities, and refine processes. Key metrics encompass not only the operational aspects of the business but also critical factors such as customer satisfaction, retention and loyalty.
Below is a comprehensive overview of critical metrics, relevance, and calculation methods:
1. Average Speed of Answer (ASA)
ASA measures the response time—the average time it takes for a call to be answered once queued. A lower ASA indicates quick response times, which lead to higher customer satisfaction and a more effective service experience.

Calculation:
ASA = Total wait time for answered calls ÷ Total number of answered calls
Best Practices:
Aiming to keep ASA low is critical for minimizing customer frustration and ensuring a positive experience. A good ASA benchmark typically falls between 15 to 30 seconds, but businesses should adjust based on the nature of their industry. However, businesses should also consider peak call volumes during busy periods, it’s reasonable for ASA to fluctuate slightly.
It’s essential to monitor ASA closely, especially during high-traffic hours, and adjust staffing or employ automated call routing to balance workload. Companies can also implement callback options to improve customer experience during high call volumes.
Example Use Case:
A telecommunications company strives to keep ASA under 20 seconds to improve customer support experience and reduce abandonment rates. They employ an intelligent call distribution system, ensuring that calls are routed to the appropriate department without delay, enhancing the overall efficiency of the call center.
2. Average Handle Time (AHT)
AHT is a composite metric that includes talk time, hold time, and after-call work. It provides insights into how efficiently agents manage interactions and resolve issues, impacting agent productivity and customer experience.
Calculation:
AHT = (Talk time + Hold time + After-call work) ÷ Total number of calls

Best Practices:
While keeping AHT low is important, it’s equally crucial to ensure that agents aren’t rushing through calls, which could impact the quality of the customer experience. Best practices involve balancing efficiency with effectiveness, meaning agents should have enough time to address all customer concerns without feeling pressured.
A good AHT range is typically 6-8 minutes, but businesses should adjust it depending on the complexity of calls. For example, support centers in e-commerce may experience shorter AHTs for basic order inquiries, while technical support teams might have longer AHTs due to more in-depth problem resolution. Furthermore, training agents to handle common queries efficiently can help reduce AHT while ensuring customers don’t feel rushed.
Example Use Case:
A customer service center in a tech support industry works to keep AHT balanced, ensuring that routine queries are resolved within 6-7 minutes. To achieve this, agents are trained to address frequent issues promptly, freeing them up to focus on more complex support requests.
3. Average Talk Time (ATT)
ATT measures the total conversation time between agents and customers. It reflects how well agents communicate, resolve issues, and manage customer expectations.
Calculation:
ATT = Total talk time ÷ Total number of calls
Best Practices:
Aiming to minimize ATT without compromising the quality of service is important. Best practices include improving agent training to ensure they can quickly and effectively resolve issues. The key is to find the sweet spot—while technical support calls often require longer ATT due to the complexity of the issues, businesses in industries like retail or finance should aim to keep ATT shorter.
Additionally, pre-call preparation equips agents with knowledge bases and scripts can help reduce ATT by allowing agents to resolve queries faster without sacrificing accuracy.
Example Use Case:
A bank’s customer service team trains agents to resolve inquiries quickly without sacrificing empathy or accuracy. The goal is to keep ATT below 5 minutes for simple queries, while more complex issues are allowed slightly longer. By optimizing processes and encouraging clear communication, ATT is kept in balance, improving overall call center efficiency.
4. After-Call Work (ACW)
ACW measures the time spent by agents on tasks after a call ends, such as documenting the interaction or updating customer records. It’s essential for evaluating agent efficiency and reducing idle time between calls.
Calculation:
ACW = Time spent on post-call work ÷ Total calls handled
Best Practices:
Reducing ACW through automation or system enhancements can significantly free up agents to handle more calls and improve overall productivity. Agents often spend time after calls updating customer information or entering notes into the system, which can be streamlined through tools such as CRM integrations or automated documentation.
Call centers can also work to reduce unnecessary post-call activities by having agents focus only on key tasks, such as updating customer records with relevant information. Another practice is ensuring that the systems agents use are easy to navigate, reducing the amount of time they spend between calls.
Example Use Case:
A call center implements automated data entry systems to reduce ACW by 30%. This allows agents to focus on assisting more customers, increasing the overall productivity of the team while maintaining quality service during calls.
5. Occupancy Rate
The occupancy rate indicates the amount of time agents are engaged in customer-related tasks, such as calls or post-call activities, compared to their available time. This metric is critical for workforce optimization and maintaining agent well-being.
Calculation:
Occupancy Rate = (Total productive time ÷ Total time available) × 100
Best Practices:
An ideal occupancy rate typically falls between 85-90%. However, it’s essential to ensure that agents aren’t overloaded, which can lead to burnout and negatively affect their performance. To maintain a healthy balance, companies should monitor occupancy rates regularly and adjust staffing based on call volume.
During high-demand periods, agents should take breaks to recharge, preventing agent fatigue and ensuring they stay productive over longer shifts. It’s also important to rotate tasks for agents, ensuring that those handling calls also take on post-call duties in a balanced way.
Example Use Case:
A tech support center carefully adjusts agent shifts to ensure a consistent occupancy rate. They use real-time data to manage workloads, ensuring agents don’t become overwhelmed during peak hours while still maintaining service levels.
6. First-Call Resolution Rate (FCR)
FCR tracks the percentage of issues resolved during the first contact. It’s a critical metric for both agent performance and customer satisfaction. High FCR rates typically correlate with fewer repeat calls and greater customer loyalty.
Calculation:
FCR = (Total resolved cases on first contact ÷ Total cases handled) × 100
Best Practices:
Achieving a high FCR rate is crucial for reducing the volume of repeat calls and enhancing customer satisfaction. To do so, it’s essential to ensure agents have the right tools, knowledge, and resources to resolve issues quickly.
This includes providing agents with comprehensive training, offering easy access to knowledge bases, and ensuring that agents are empowered to make decisions during calls. It’s also important to monitor FCR continuously and adjust training or systems as needed to improve resolution rates.
Example Use Case:
An insurance company focuses on training agents to handle complex claims within a single call. With a robust knowledge base and decision-making guidelines in place, FCR rates increase, leading to a reduction in repeat calls and an overall improvement in customer satisfaction.
7. Customer Satisfaction Score (CSAT)
CSAT, or Customer Satisfaction Score, is a key metric used to assess how happy customers are with their experience at the call center. It’s typically measured through post-interaction surveys that focus on how effectively agents meet customer needs. These insights help you evaluate service quality and pinpoint areas for improvement.

CSAT directly reflects customer sentiment following a support interaction or a purchase. To calculate your CSAT score, consider asking your customers questions such as:
- Were you satisfied with the support you received? (Yes/No)
- How would you rate your satisfaction on a scale of 1 to 10 with the service you received?
- How satisfied are you with the outcome of this interaction? (Unsatisfied, Neutral, Satisfied)
To compute CSAT, count the number of positive responses (e.g., “Satisfied” or “Very Satisfied”) and divide that by the total number of responses received. Multiply the result by 100 to get the percentage of satisfied customers.
Calculation:
CSAT = (Total number of positive responses / Total number of responses collected) * 100
Best Practices:
To maintain high CSAT scores, it’s important to analyze survey results regularly to identify dissatisfaction trends and address common pain points. A CSAT score of 85% or higher is generally considered an excellent benchmark.
Best practices include offering personalized customer service, ensuring quick resolutions, and maintaining clear communication throughout the customer journey. Additionally, acting on customer feedback and making improvements where needed is crucial for long-term customer retention.
Example Use Case:
A retail company uses CSAT surveys to track customer feedback after every interaction. By consistently receiving positive responses and addressing any customer concerns, the company maintains a CSAT score above 90%, ensuring high customer loyalty and repeat business.
8. Net Promoter Score (NPS)
NPS measures customer loyalty and is an indicator of overall brand sentiment. It evaluates how likely customers are to recommend a company to others, which can be a strong predictor of long-term business success.
Calculation:
Net Promoter Score = Percent of promoters – Percent of detractors
Best Practices:
Regularly measuring NPS allows businesses to identify areas for improvement and implement strategies to enhance customer loyalty. A positive NPS score indicates strong brand advocacy, while a negative score may highlight customer dissatisfaction.
To improve NPS, focus on enhancing the customer experience across all touchpoints, from the initial interaction to post-call follow-ups. Personalized service, proactive communication, and addressing issues effectively are essential to improving NPS over time.
Example Use Case:
A cloud service provider uses NPS to track customer sentiment after each interaction. By focusing on delivering superior customer service and solving technical problems promptly, the company improves its NPS, ultimately leading to higher customer loyalty and retention.
9. Customer Effort Score (CES)
CES measures how much effort customers must expend to resolve an issue with the company. A low CES indicates that customers are able to resolve their concerns with minimal hassle, which correlates with higher satisfaction.
Calculation:
Typically rated on a scale of 1 to 5, with 1 being low effort and 5 being high effort
Best Practices:
To minimize customer effort, businesses should focus on streamlining processes, offering self-service options, and ensuring that agents have the necessary tools to resolve issues quickly. Reducing the number of steps customers need to take to resolve an issue can significantly improve their experience. By minimizing friction in the support process, companies can improve customer satisfaction and reduce churn.
Example Use Case:
A bank reduces CES by providing more self-service options on its mobile app. Customers can easily access their account information, perform transactions, and resolve simple issues independently, significantly reducing the effort needed to get support.
10. Average Hold Time
Average hold time measures how long customers are left waiting on the phone before speaking with an agent. High hold times can lead to customer frustration and call abandonment, so minimizing this metric is crucial for maintaining a positive customer experience.
Calculation:
Average Hold Time = Total hold time ÷ Total number of calls
Best Practices:
Strive to keep hold times as short as possible—ideally under 2 minutes. Companies can achieve this by optimizing staffing levels during peak hours, using automated call routing, and providing customers with an option to receive a callback instead of waiting on hold.
Additionally, ensure that self-service channels are available for routine queries, allowing customers to resolve issues without the need to speak to an agent. Monitoring call flow and identifying bottlenecks can also help reduce overall hold times.
Example Use Case:
A customer service center for a tech company analyzes peak call volumes and adjusts staffing accordingly. By increasing agent availability during busy hours and offering callback options, they reduce hold times and improve customer satisfaction.
11. Transfer Rate
The transfer rate measures how often calls are transferred to another agent or department. A high transfer rate can indicate poor training, ineffective call routing, or lack of agent expertise, all of which can negatively impact the customer experience.
Calculation:
Transfer Rate = (Total transferred calls ÷ Total calls) × 100
Best Practices:
Aiming to minimize the transfer rate is crucial for providing seamless customer service. Implementing cross-training for agents so they can handle a variety of customer issues is key to reducing unnecessary transfers.
Investing in advanced call routing technology ensures that calls are directed to the right department the first time, avoiding multiple transfers. Reducing transfers also helps to enhance first-call resolution rates and customer satisfaction.
Example Use Case:
A health insurance provider reduces its transfer rate by implementing a cross-training program for agents. This allows agents to resolve a broader range of customer queries without needing to escalate or transfer calls, leading to better customer experiences.
12. Escalation Rate
The escalation rate tracks how often calls are escalated to a supervisor or higher-level support team. A high escalation rate can indicate that agents lack training or decision-making authority, leading to delays in problem resolution.
Calculation:
Escalation Rate = (Total escalated calls ÷ Total calls) × 100
Best Practices:
Empowering agents to make decisions and resolve issues independently is key to reducing escalation rates. Providing agents with the right tools, knowledge, and autonomy can help them handle complex issues without needing to escalate. Additionally, regular training and the use of knowledge bases ensure that agents are well-equipped to resolve a wide range of issues effectively.
Example Use Case:
A utility company reduces escalation rates by providing agents with an extensive knowledge base and clear guidelines for resolving technical issues. This enables agents to handle more calls independently, improving overall call center efficiency and customer satisfaction.
13. Repeat Contact Rate
The repeat contact rate measures how often customers contact the call center about the same issue after an initial resolution. A high repeat contact rate can indicate that issues are not being fully resolved the first time, leading to customer frustration and additional workload for agents.
Calculation:
Repeat Contact Rate = (Total repeat contacts ÷ Total contacts) × 100
Best Practices:
To reduce repeat contact rates, it’s important to ensure that issues are resolved thoroughly during the first call. Providing agents with comprehensive training and problem-solving tools can help prevent issues from recurring. Agents should verify that all customer concerns are addressed before ending a call. Monitoring repeat contacts and identifying common reasons for follow-up calls can also help to improve the resolution process.
Example Use Case:
A telecommunications company reduces repeat contact rates by improving the troubleshooting guides provided to agents. These guides help agents resolve common issues on the first call, reducing the likelihood of customers needing to follow up.
14. Agent effort score
Call quality monitoring evaluates how well agents adhere to quality standards during customer interactions, including aspects like tone, professionalism, and compliance with company policies. This metric is essential for ensuring consistent service quality.

Calculation:
Agent effort score = Sum of survey scores / Number of respondents
Best Practices:
Regular monitoring and feedback are crucial for maintaining high standards. Companies should provide agents with constructive feedback and conduct regular training to reinforce desired behaviors.
Quality assurance programs that focus on adherence to scripts, active listening, and problem-solving can improve both the quality of customer interactions and agent performance. Additionally, incorporating customer feedback into evaluations ensures that the service meets customer expectations.
Example Use Case:
A financial services company uses call quality monitoring to evaluate agents’ adherence to regulatory compliance and professionalism. By providing agents with regular feedback and ongoing training, the company ensures that all customer interactions meet high-quality standards.
15. Script Adherence Rate
Script adherence measures how well agents follow prescribed scripts or guidelines when interacting with customers. This is particularly important for ensuring that compliance is maintained and that customers receive consistent messaging.
Calculation:
Script Adherence Rate = (Number of calls where the script was followed ÷ Total calls) × 100
Best Practices:
While flexibility is important, agents should follow scripts to ensure consistency and compliance across all customer interactions.
Companies should provide scripts that allow for personalization while still covering key messages, ensuring that agents can deliver information clearly and effectively. Additionally, monitoring script adherence and providing agents with regular feedback helps maintain high standards.
Example Use Case:
A telecom company monitors script adherence to ensure that agents communicate key compliance messages during customer calls. Regular training and feedback help agents balance script-following with personalization, ensuring both compliance and customer satisfaction.
16. Schedule Adherence
Schedule adherence measures whether agents follow their assigned schedules, including breaks, work periods, and shift times. High schedule adherence is crucial for ensuring workforce optimization and maintaining service levels.
Calculation:
Schedule Adherence = (Time spent working as scheduled ÷ Total scheduled time) × 100
Best Practices:
High schedule adherence is key to maintaining service levels and avoiding staffing shortages. Companies can improve adherence by monitoring real-time data, adjusting shifts dynamically, and ensuring that agents are aware of expectations.
It’s important to strike a balance between flexibility for agents and ensuring that the center operates smoothly. Offering shift flexibility and using real-time analytics to adjust staffing can improve adherence.
Example Use Case:
A contact center uses real-time data to adjust shift schedules based on incoming call volume. By increasing staffing during peak hours and optimizing break schedules, the center ensures high schedule adherence, improving overall service levels.
17. Conversion Rate
The conversion rate measures how often customer interactions result in a desired action, such as making a purchase, upgrading a service, or subscribing to a product. It’s crucial for sales-driven call centers.
Calculation:
Conversion Rate = (Number of successful conversions ÷ Total interactions) × 100
Best Practices:
To optimize conversion rates, businesses should focus on personalizing interactions, using effective sales scripts, and training agents to identify and address customer needs. Monitoring conversion metrics and adapting strategies based on performance is also key to improving results. Additionally, using upselling or cross-selling techniques can increase the chances of successful conversions.
Example Use Case:
An e-commerce company tracks conversion rates to measure the effectiveness of its sales campaigns. By training agents to offer personalized recommendations during calls, the company increases its conversion rate and boosts sales.
18. Average Order Value (AOV)
AOV measures the average value of orders placed during customer calls. This is particularly important for sales-driven call centers, where the goal is to maximize revenue per customer interaction.

Calculation:
AOV = Total revenue from orders ÷ Total number of orders
Best Practices:
Encouraging agents to upsell or cross-sell during calls is a key strategy for increasing AOV. Additionally, businesses should ensure agents are trained to identify customer needs and suggest complementary products or services. By optimizing the customer journey and providing.
Example:
A call center for an online electronics store noticed customers often bought laptops without accessories. To boost AOV, agents were trained to suggest related items like laptop bags, wireless mice, or extended warranties during calls.
With this simple approach, combined with a CRM that highlighted customer preferences, the center saw an increase in AOV within three months—all by focusing on helpful recommendations instead of pushy sales tactics.
How to Effectively Track Call Center Agent Performance Metrics
Tracking and measuring performance metrics is vital to maintaining optimal efficiency and delivering exceptional service. To effectively track call center agent productivity and optimize performance, it’s essential to invest in the right call center software.
Here are the key features to consider when choosing a solution for your business:
1. Real-time Analytics and Reporting
Modern call center solutions empower businesses to track key performance metrics such as Average Call Duration (ACD), Average Call Handling Time (AHT), and Call Abandonment Rate. Real-time dashboards and reports provide valuable insights into ongoing calls, queue status, agent availability, and SLA compliance.

With detailed interaction metrics for calls, emails, and chats, these solutions help businesses enhance agent performance and elevate customer satisfaction.This helps businesses make quick, informed decisions, ensuring alignment with service goals and operational efficiency.
2. CRM Integration
Integrating a customer relationship management (CRM) system with your call center software provides agents with a unified view of customer information, such as contact details, case numbers, interaction history, and case statuses.
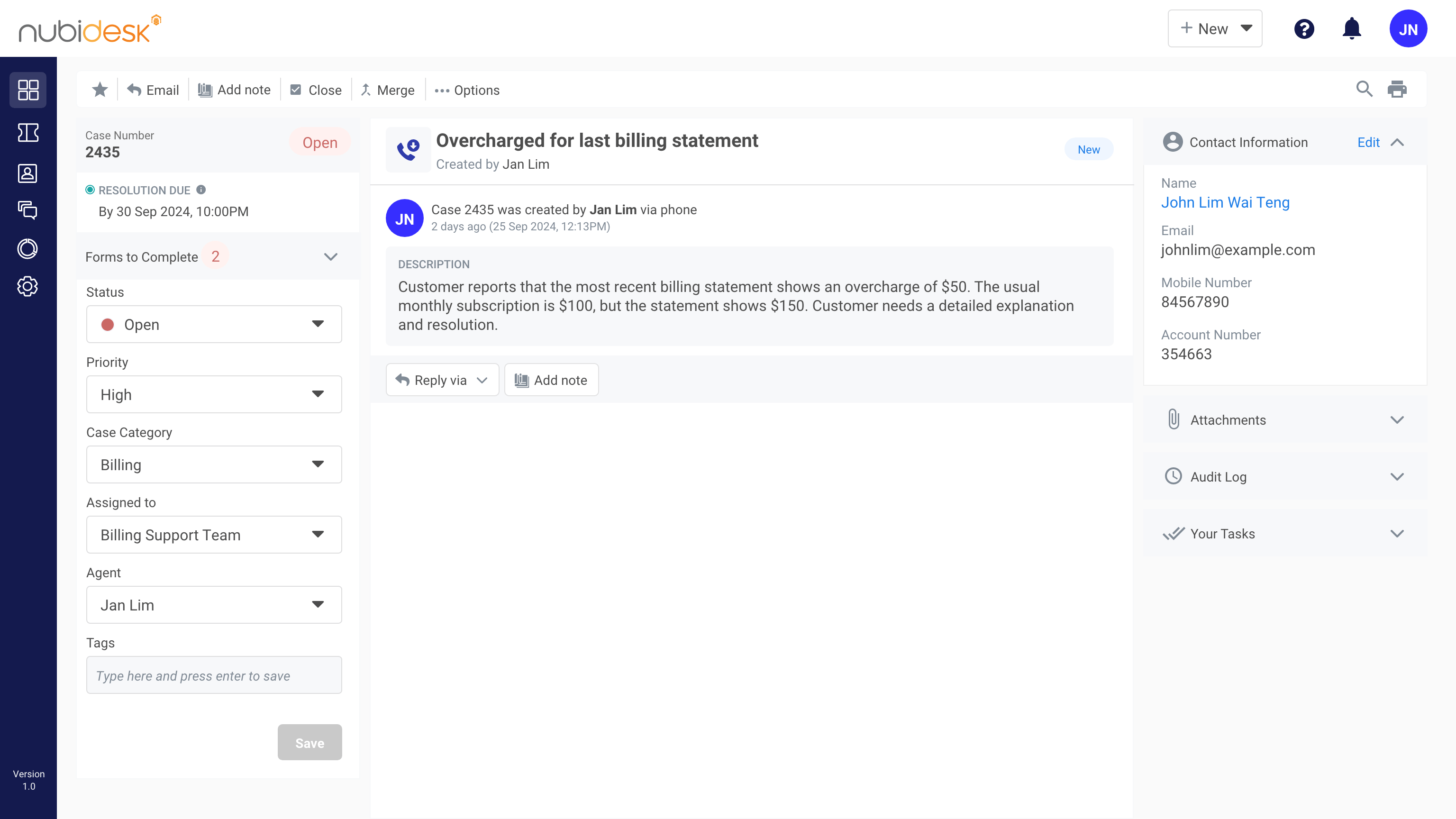
This seamless integration enhances case management solutions by enabling agents to resolve issues like billing discrepancies efficiently, ensuring faster turnaround times, improved SLA compliance, and higher customer satisfaction.
3. Conversation Analytics
Modern call center solutions offer conversation analytics powered by Gen AI, including features like automatic speech recognition, sentiment analysis, and customer intent tracking.
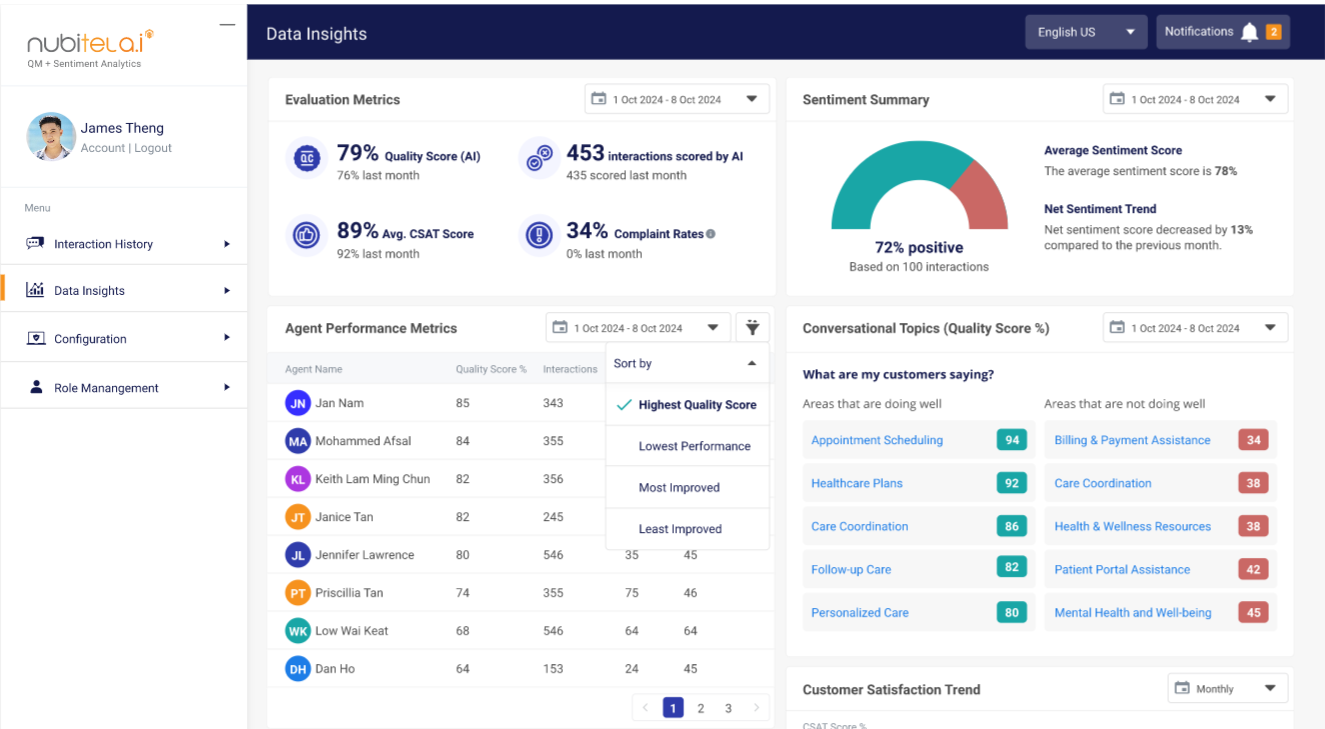
This allows businesses to identify patterns in both customer interactions and agent performance in real-time. With quality monitoring tools, businesses can record, evaluate, and provide feedback on calls to enhance agent performance.
Contact center supervisors can have a deeper look into conversation analytics, it’s worth exploring various solutions available in the market.
By leveraging these tools, businesses can monitor key metrics, track agent performance seamlessly, and use data-driven insights to improve customer satisfaction. These features ensure that call centers operate efficiently, improve agent performance, and contribute to better overall customer outcomes.
How to Boost Call Center Agent Performance
Improving agent performance requires actionable strategies supported by technology and training. Consider the following methods:
- Leverage Real-Time Call Monitoring for Proactive Coaching
Supervisors can review ongoing calls to provide instant feedback, enhancing agent response quality and confidence. - Invest in AI and Automation for Better Efficiency
Implement technologies such as predictive analytics and intelligent call routing to optimize workflows and reduce agent workloads. - Recognize and Reward Excellence to Motivate Agents
Establish performance-based recognition programs tied to metrics like FCR and CSAT to incentivize agents. - Implement Skill-Based Routing for Better Resolution Rates
Match customer queries to the most knowledgeable agents to ensure efficient and satisfactory resolutions. - Hold Daily Huddles for Enhanced Communication
Facilitate brief team meetings to discuss goals, share updates, and address challenges collaboratively. - Continuously Review and Refine Key Performance Indicators
Regularly evaluate KPIs to align them with evolving customer and business needs. - Prioritize Comprehensive Training and Development
Offer ongoing education programs to equip agents with skills and knowledge to handle diverse customer interactions effectively.
Conclusion
In conclusion, tracking call center agent performance is key to delivering high-quality service and improving efficiency. Tools like real-time analytics, CRM integration, and workforce management provide valuable insights into agent productivity and customer satisfaction. By leveraging these insights, businesses can make informed decisions, empower agents, and enhance customer experiences, ultimately driving continuous improvement and operational success.





