Contact centers are a core part of modern customer service, providing the essential infrastructure for businesses to engage with their customers. The evolution from traditional call centers to advanced, cloud-based contact centers has dramatically transformed how companies interact with clients. In this article, we explore the various types of contact centers, their features and how they improve operational efficiency and customer satisfaction.
Table of Contents
ToggleWhat Is a Contact Center?
A contact center is a centralized hub where businesses manage all customer interactions across multiple communication channels like phone calls, emails, chat, social media, and SMS. Unlike traditional call centers that mainly handle voice calls, modern contact centers provide a more integrated, multichannel approach to customer service and engagement.
There are different aspects to a contact center:
- Contact Center Software: This includes the programs used by agents to manage customer interactions. It encompasses features like call handling, real-time reporting, queue visualization, and more. With these tools, agents can provide faster and more efficient service across various communication channels.
- Contact Center as a Service (CCaaS): In the cloud-based era, CCaaS is the deployment model for contact center software. Much like how Netflix or Spotify deliver services over the internet, CCaaS offers all necessary features and functionality without the need for on-premises equipment. Businesses can scale easily and update features without worrying about physical infrastructure.
- Contact Center Department: This is the team of professionals responsible for using the contact center software. It includes agents who manage customer interactions across various platforms, as well as management and specialist roles like quality assurance and resource planning. These teams work together to ensure that the contact center operates smoothly and meets customer expectations.
Modern contact centers also leverage AI-powered virtual assistants and CRM integrations to deliver seamless, personalized customer experiences. These solutions enable businesses to provide fast, accurate support while gaining valuable insights from customer data throughout the entire journey.
Contact Center vs. Call Center: So What Are the Differences?
While call centers and contact centers often share similar functions, it’s important to recognize the distinct differences between the two.
Both types of centers aim to provide customer support, but call center software is focused solely on managing phone interactions. It routes calls to various departments, often with the assistance of Voice over Internet Protocol (VoIP) technology.
On the other hand, a contact center goes beyond just calls. It integrates multiple communication channels—such as phone, email, chat, messaging apps, social media, and even self-service portals. This flexibility allows you to meet your customers wherever they are, providing seamless support across various touchpoints.
| Feature | Contact Center | Call Center |
| Communication Channels | Voice, Email, Chat, Social, SMS, WhatsApp | Primarily Voice |
| Customer Interaction | Omnichannel | Single-channel (Voice) |
| Technology Integration | CRM, AI, Chatbots, Analytics | Basic Telephony |
| Flexibility | Cloud-based, Scalable | On-premises or Limited Remote |
| Customer Experience | Seamless, Data-driven | Linear, Transactional |
5 Types of Contact Centers
Explore the various types of contact centers to find the best match for your business and customer needs.
1. Inbound Contact Center
An inbound contact center handles incoming communications from customers. Agents typically manage queries related to:
- Product support
- Promotions
- Business hours and locations
- Account information
- Payment processing
Example: A medical clinic uses an inbound contact center to manage appointment bookings and respond to queries about opening hours. A software company uses it to provide technical support via live chat, email, or video tutorials.
2. Outbound Contact Center
Outbound contact centers initiate contact with customers, usually for:
- Sales and promotions
- Appointment setting
- Lead generation
- Fundraising
- Payment collections
- Customer surveys
Agents often use power dialers or predictive dialers to speed up the process.
Example: A telco company uses its outbound team to promote new mobile plans and collect feedback through post-sale surveys.
3. Multichannel Contact Center
Multichannel contact centers support several communication channels—phone, chat, email, SMS, and social media. However, these systems often work in silos, meaning customer data may not carry across channels.
Example: A customer initiates a support request via live chat, then follows up via email. If the multichannel system isn’t integrated, the agent handling the email may not have access to the chat history.
4. Omnichannel Contact Center
Omnichannel centers offer a seamless experience across channels. Data is centralized, enabling agents to view full customer interaction history, regardless of platform.
Example:
A customer reaches out to a retail brand via Facebook Messenger, escalates the issue through email, and later receives a follow-up call. With the Agent Workbench, the agent handling the interactions has instant access to the complete interaction history, ensuring a smooth, personalized experience and maintaining continuity across all touchpoints.
5. On-Premises Contact Center
This model uses local infrastructure hosted within the company’s physical premises. While it offers complete control over data and systems, it requires high upfront costs and ongoing maintenance.
Benefits:
- No monthly subscription
- Full hardware/software control
- On-site data storage
Limitations:
- Costly to scale
- Limited flexibility
- Requires dedicated IT staff
6. Cloud-Based Contact Center
A cloud-based contact center operates over the internet. It offers high flexibility, rapid deployment, and lower costs.
Advantages:
- Scalable infrastructure
- Remote agent support
- Real-time analytics
- Centralized customer data
Example: A startup uses a cloud-based contact center to support a global customer base with agents working remotely from different time zones.
6 Benefits of a Contact Center
A contact center allows support agents to engage with customers across multiple channels. This not only enhances convenience for customers but also provides more ways to understand their needs and deliver better service. Here are six key benefits your business can gain from using a contact center.
1. Delivers Omnichannel Support
Agents can offer better service with a full view of customer interactions. Omnichannel systems consolidate information from live chats, emails, and calls into one dashboard.
Example: A customer chats with a bot about an issue. The conversation is escalated to a live agent, who continues seamlessly without the customer repeating details. This minimizes friction and accelerates resolution.
2. Improves Customer Satisfaction
Customers can choose their preferred support channel, whether it’s voice, chat, or email. Agents use historical data to provide personalized service.
Example: A customer prefers chat for general inquiries but chooses a call for urgent matters. The contact center enables both, enhancing satisfaction.
3. Promotes Internal Collaboration
A centralized contact center platform enhances team communication and knowledge sharing.
Example: An agent handling a complex case consults with billing and account teams in real time. Together, they resolve the issue within an hour and streamline a recurring billing error.
4. Increases Sales Opportunities
Contact centers open up multiple touchpoints for upselling and cross-selling.
Example: During a laptop support call, an agent learns the customer needs better performance. The agent suggests a new model and extended warranty. The customer agrees—resulting in an upsell.
5. Gathers Customer Insights
Contact centers use analytics tools to track behavior across channels and identify common pain points.
Example: A financial firm notices an increase in chatbot queries about suspicious transactions. They use this data to improve fraud alerts and update their FAQ section.
6. Offers Cost Efficiency
Cloud-based contact centers reduce infrastructure and operational costs. They also enable faster deployment and flexible staffing.
Example: An e-commerce brand scales its support team during seasonal sales using cloud-based tools, avoiding expensive hardware investment.
6 Key Contact Center Use Cases
Contact centers do more than just handle inquiries — they create meaningful customer connections, simplify daily operations, and strengthen brand loyalty. Whether it’s through AI-powered self-service or tailored, one-on-one support, today’s businesses are using contact centers to meet customers exactly where they are. The result? Smoother experiences and happier customers. Below are six key use cases that highlight just how transformative modern contact centers can be.
1. Proactive Customer Engagement
Proactive customer engagement involves reaching out to customers before they even contact you. By anticipating customer needs or addressing potential issues in advance, you can enhance their experience and increase satisfaction. This approach can take many forms, including personalized follow-ups, product recommendations, reminders, and even alerts about account status or service disruptions.
Example: Imagine a telecom provider uses a contact center to proactively inform customers about an upcoming service outage in their area. Before the customer even notices a disruption, the company sends an automated message or email with the details of the issue, steps being taken, and how the customer can manage their account or resolve the problem. This not only reduces customer frustration but also helps manage expectations and enhances trust in the service provider.
Additionally, this proactive approach can include sending targeted marketing campaigns or reminders, such as for contract renewals, to retain customers or prevent churn.
2. Outbound Sales and Lead Generation
Outbound contact centers are often used to reach out to potential customers, whether for sales, surveys, promotions, or research. By using automated dialers and customer databases, agents can quickly initiate contact with prospects, delivering tailored pitches or information to specific target groups.
Incorporating advanced CRM systems allows contact center agents to track the status of these prospects and build a complete picture of each customer’s journey. Through outbound contact, agents can nurture relationships, qualify leads, and convert them into loyal customers. This can be especially effective in industries such as retail, real estate, and finance, where lead generation plays a pivotal role in business growth.
Example: A software company may use an outbound contact center to follow up on inquiries about a free trial, offering a personalized demo or a discount to encourage prospects to convert into paying customers. By integrating data from their CRM, the agent can tailor the conversation based on the customer’s previous interactions or behavior, improving the chances of conversion.
3. AI-Powered Self-Service (Artificial Intelligence)
As customer expectations for speed and convenience continue to rise, many contact centers are adopting AI-powered self-service solutions driven by Conversational AI to handle routine interactions more efficiently. These include intelligent virtual assistants that can address common requests like password resets, order tracking, and basic troubleshooting—without the need for live agent intervention.
According to Gartner, by 2026, Conversational AI deployments within contact centers will reduce agent labor costs by $80 billion. These AI technologies not only offer round-the-clock availability but also accelerate response times, significantly enhancing customer satisfaction and boosting operational efficiency.
Example: A customer contacting an online retailer’s contact center to inquire about the status of their order may first interact with an AI-powered virtual assistant. The virtual assistants checks the order status in real-time and provides the customer with immediate answers, helping them avoid long wait times. If the customer requires further assistance, the system smoothly hands over the conversation to a live agent, who already has the context of the interaction.
4. Omnichannel CX Management
Omnichannel customer experience (CX) management refers to the ability to provide a consistent, personalized experience across all communication channels. With an omnichannel contact center, customers can switch between different methods of communication—like chat, email, or social media—without losing the context of the conversation.
This approach ensures that no matter how customers interact with your business, the experience feels cohesive, relevant, and tailored to their needs. It also allows agents to provide more informed responses since all interactions are recorded and can be referenced across channels.
Example: A customer might start by messaging a business on Instagram to inquire about a product, then later follow up via email with more detailed questions. An omnichannel contact center ensures that the agent handling the email knows the context of the Instagram conversation and can provide a seamless, continuous experience, rather than asking the customer to repeat themselves.
5. AI-Driven Customer Conversation Analytics Dashboard
AI-driven conversation analytics helps contact centers track and understand every step of the customer journey. By collecting data from voice calls, digital channels, and customer feedback, teams can uncover insights into behavior, sentiment, and service quality.
With a clear view of what’s working and where support is falling short, businesses can adjust strategies, improve agent performance, and deliver more consistent service. Monitoring trends like sentiment scores, topic quality, and complaint rates also allows for faster, data-backed decision-making.
Example: A healthcare provider’s contact center noticed from the conversational topics dashboard that “mental health support” had a lower quality score and a higher complaint rate compared to topics like “appointment scheduling” or “healthcare plans.” With this insight, the team provided targeted agent training and updated response guidelines. Within weeks, quality scores improved and sentiment shifted from negative to neutral and positive, resulting in higher customer satisfaction.
6. Hyper Personalized Support
In a world where personalization is key to customer satisfaction, contact centers are focusing on delivering hyper personalized support—tailoring interactions based on the customer’s history, preferences, and behavior. By integrating data from CRM systems, transaction histories, and previous touchpoints, agents can offer a level of service that makes customers feel understood and valued.
Hyperpersonalization can include addressing the customer by name, referring to past issues or purchases, or even suggesting relevant products or services that align with their needs. This approach helps strengthen customer relationships and fosters brand loyalty.
Example: A customer contacts a fashion retailer’s contact center about an issue with a recent order. Using data from the company’s CRM system, the agent can access the customer’s past purchases, including size, color preferences, and previous returns. By acknowledging this history and offering personalized solutions (such as recommending a new item in the customer’s preferred color), the agent can provide a more meaningful, tailored experience that increases the likelihood of retaining the customer.
Contact Center Technology & Features
Contact centers today rely on advanced technologies to deliver efficient and scalable customer service. The right combination of tools, systems, and features can significantly improve agent performance, streamline operations, and enhance the overall customer experience. Here’s a deeper dive into the essential technologies and features that power modern contact centers.
1) CRM System
A Customer Relationship Management (CRM) system is the backbone of a contact center, consolidating all customer information and interactions into a single platform. By integrating the CRM system with various communication channels, agents can access customer history, preferences, and past interactions in real-time, allowing for more personalized support. A robust CRM helps improve customer satisfaction, track key metrics, and ensure timely responses.
2) Inbound Call Routing
Inbound call routing directs incoming calls to the most appropriate agent based on predefined criteria, such as the customer’s issue, language preference, or previous interactions. This feature ensures that customers are connected to agents with the expertise to resolve their inquiries quickly, reducing wait times and improving first-call resolution rates. Modern inbound call routing systems can also consider factors such as agent availability and skillset.
3) Advanced Call Routing (ACD) and Routing
Automatic Call Distribution (ACD) is a sophisticated routing technology that goes beyond simple inbound call routing. ACD systems can dynamically route calls based on more advanced factors such as customer behavior, issue complexity, or priority status. By integrating with other systems like CRM and workforce management tools, ACD can ensure that customers are directed to the right resources, improving operational efficiency and customer satisfaction.
4) Call Recording
Call recording enables businesses to capture and store audio recordings of customer interactions. This technology plays a crucial role in quality assurance, training, and compliance. With the ability to review past calls, managers can assess agent performance, identify areas for improvement, and ensure that agents are adhering to company policies. Call recording also serves as a valuable resource for dispute resolution and regulatory compliance.
5) Call Monitoring
Call monitoring allows supervisors to listen to live calls between agents and customers, providing real-time insights into service quality and agent performance. Supervisors can provide on-the-spot coaching or intervene if needed to ensure a positive customer experience. This feature is essential for maintaining high service standards and improving the skills of customer support agents.
6) Knowledge Base Integration
A knowledge base integration allows agents to access a repository of frequently asked questions (FAQs), product manuals, troubleshooting guides, and best practice articles directly within their contact center software.
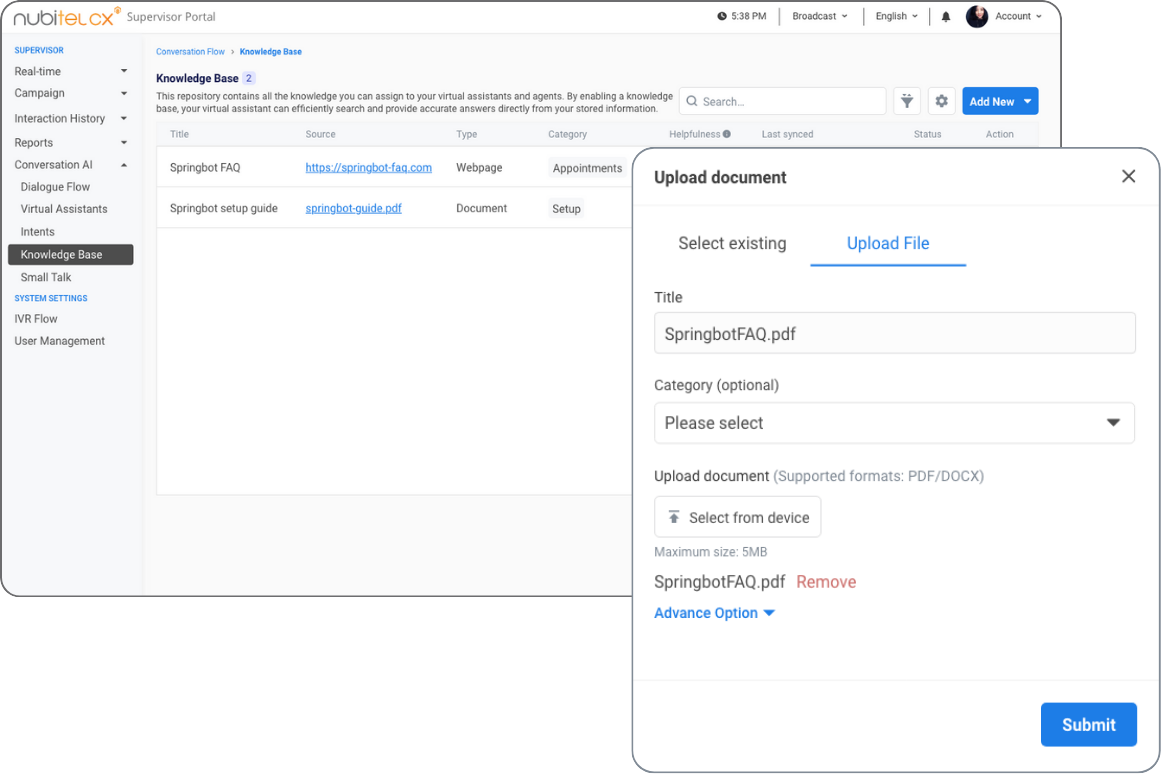
By leveraging knowledge base resources, agents can resolve customer inquiries more quickly and accurately, reducing call handling time and improving first-contact resolution rates.
7) Real-Time Reporting
Real-time reporting is a crucial feature that provides managers and supervisors with live data on key performance indicators (KPIs) such as call volume, wait times, agent availability, and service level performance. By analyzing these real-time metrics, decision-makers can make adjustments to staffing, resources, or workflow processes to optimize performance and ensure service level agreements (SLAs) are being met.
8) Conversation Analytics
Conversation Analytics involves the use of artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML) algorithms to analyze customer interactions in real time.
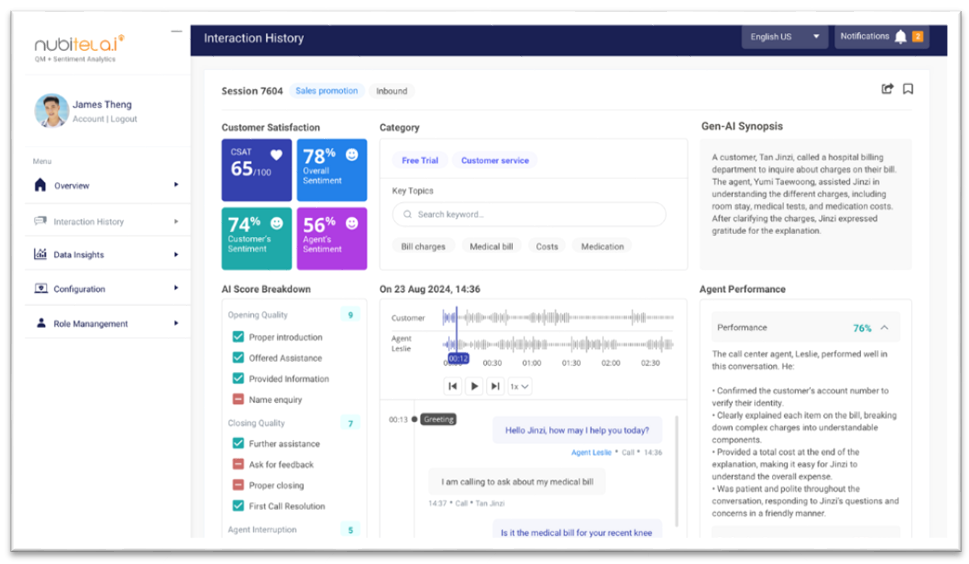
By transcribing and analyzing calls, chats, or messages, conversational analytics can identify customer sentiment, detect common issues, and provide actionable insights for improving customer service. This feature enables contact centers to better understand customer needs and adjust their strategies accordingly.
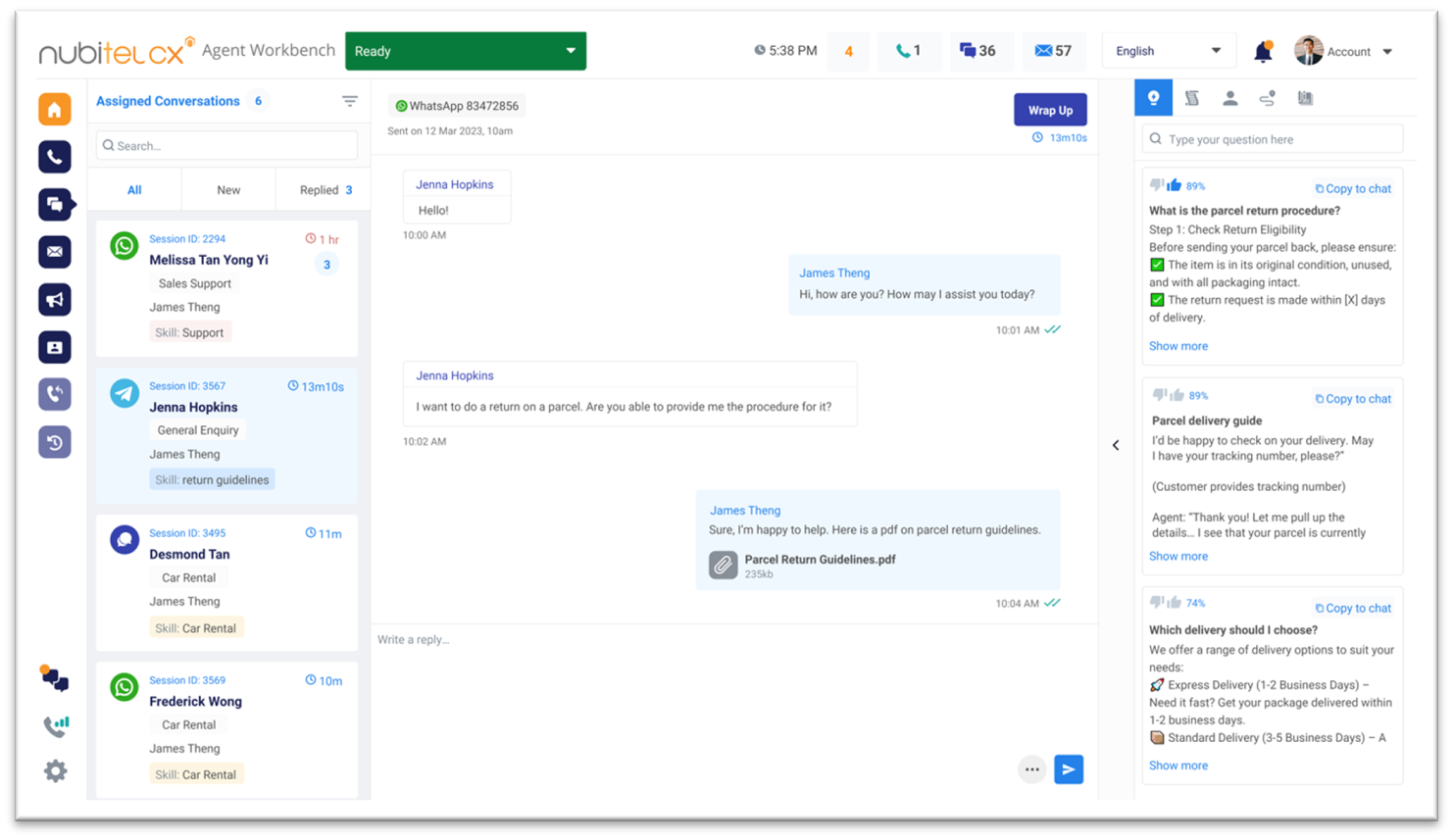
9) AI Agent
AI agents, powered by Natural Language Processing (NLP) and Large Language Models (LLM), are designed to handle both voice and chat interactions. For voice, AI agents can manage customer inquiries using speech recognition and generate spoken responses.
For chat, they can engage in text-based conversations, providing instant support. With the integration of Retrieval-augmented Generation (RAG), AI agents retrieve data from a knowledge base to generate contextually relevant, accurate responses. These AI agents can also assist live agents in real-time by offering suggestions or handling routine queries, improving efficiency and customer satisfaction.
How to Develop a Contact Center Strategy
Developing a robust contact center strategy is crucial to ensuring efficient operations, high customer satisfaction, and the achievement of business goals. The following steps can help businesses build a strategic plan that meets both customer expectations and organizational objectives:
1. Define Business Objectives
The first step in developing a contact center strategy is understanding the broader business objectives. This could include improving customer retention, increasing sales, enhancing operational efficiency, or ensuring compliance with industry regulations. By aligning contact center goals with company-wide objectives, businesses can ensure their efforts are contributing directly to overall success.
2. Understand Customer Needs
A key component of any contact center strategy is understanding the needs and expectations of your customers. Collect feedback through surveys, social media, and direct interactions to gauge customer satisfaction levels, identify pain points, and understand their preferred communication channels. This customer-centric approach will guide the design of a strategy that prioritizes customer experience.
3. Choose the Right Technology
Selecting the right tools and technologies is vital to building an effective contact center strategy. Whether it’s CRM systems, omnichannel platforms, or AI-powered solutions, ensure that the technologies you choose integrate seamlessly with your existing operations. Prioritize tools that help streamline processes, reduce response times, and improve the quality of customer interactions.
4. Establish Performance Metrics
Measuring success is key to refining a contact center strategy over time. Set clear Key Performance Indicators (KPIs) such as average handling time (AHT), customer satisfaction (CSAT), first call resolution (FCR), and service level agreements (SLAs). These metrics will help you track progress and pinpoint areas that require improvement.
5. Develop Training and Coaching Plans
Investing in ongoing agent training and coaching is critical to achieving high service standards. Create training programs that focus on product knowledge, communication skills, and empathy. Continuous coaching will help agents adapt to new technologies, stay up to date with best practices, and improve customer interactions.
6. Monitor and Optimize
Finally, consistently monitor performance data, customer feedback, and industry trends to identify opportunities for optimization. Adapt the strategy as necessary to ensure the contact center is agile and responsive to both customer demands and business needs. Regularly assess your strategy’s effectiveness and make data-driven decisions to improve service delivery.
The Future of Contact Centers
The future of contact centers is being revolutionized by AI-powered solutions and the increasing demand for hyper personalized customer experiences. As the hype surrounding generative AI (GenAI) continues to grow, its adoption is rapidly becoming a priority for customer service leaders.
In fact, 85% of customer service leaders are planning to explore or pilot generative AI solutions to enhance customer interactions by 2025. These technologies will be instrumental in transforming contact centers by enabling seamless voice and chat support, improving agent productivity, and delivering more personalized experiences for customers.
At Nubitel, we are prepared to help provide cloud contact center solutions stay ahead of the curve. Let’s schedule a demo today to explore how we can enhance your customer experience.





